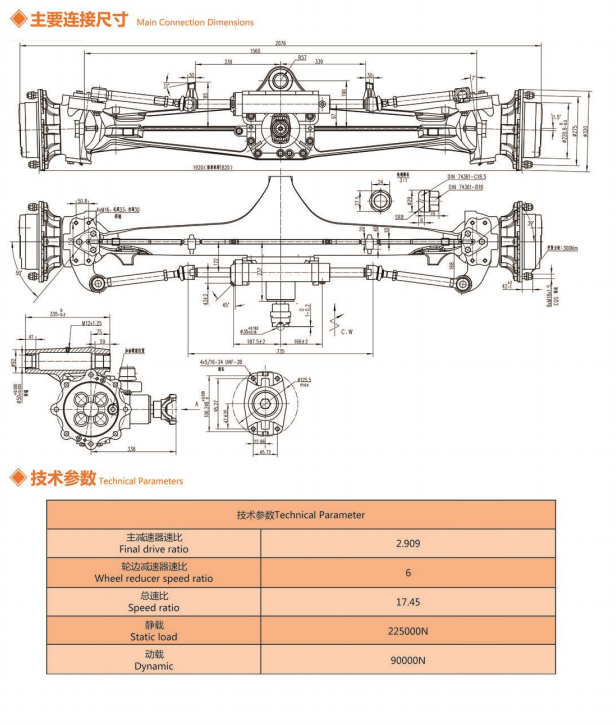
WZD75-100 Axle
Applicable to construction machinery, wheeled excavator loader (both ends busy) drive axle
The drive axle is at the end of the power transmission system, and its basic functions are: (1) transmitting the engine torque from the universal transmission device to the drive wheel through the main reducer, differential, half shaft, etc., to reduce speed and increase torque; (2) Change the transmission direction of torque through the bevel gear pair of the main reducer; (3) The differential realizes the differential of the wheels on both sides to ensure that the inner and outer wheels steer at different speeds; (4) The bearing and torque transmission functions are realized through the bridge shell and wheels.
The drive axle design should meet the following basic requirements:
1. The main reduction ratio selected should ensure that the car has the best power and fuel economy.
2. The overall dimension should be small, and the necessary ground clearance should be ensured. It mainly refers to the size of the main reducer as small as possible.
3. Gears and other transmission parts work smoothly and have low noise.
4. High transmission efficiency under various speeds and loads.
5. Under the condition of ensuring sufficient strength and stiffness, the mass should be small, especially the unsprung mass should be as small as possible to improve the smoothness of the car.
6. Coordinate with the movement of the suspension guide mechanism, and for the steering axle, it should also coordinate with the movement of the steering mechanism.
7. Simple structure, good processing technology, easy manufacturing, easy to disassemble and adjust.
The drive axle is divided into two categories: non-disconnected type and disconnect type.
It is not disconnected
When the drive wheels are non-independent suspension, a non-disconnected axle should be selected. The non-disconnected drive axle is also called the integral drive axle, and its half shaft casing and main reducer shell are rigidly connected to the axle shell and a monolithic beam, so that the half axle and drive wheel on both sides swing in relation to each other, and are connected to the frame through elastic elements. It consists of a drive axle housing, a main reducer, a differential and a half shaft.
Disconnected
The drive axle adopts independent suspension, that is, the main reducer shell is fixed on the frame, and the half axle and drive wheel on both sides can have relative movement in the transverse plane relative to the car body, which is called a disconnected drive axle.
To mate with the independent suspension, the main reducer housing is fixed to the frame (or body), the drive axle housing is segmented and connected by hinges, or there are no other parts of the drive axle housing except the main reducer housing. In order to meet the needs of independent up and down runout of the drive wheel, the sections of the half-shaft between the differential and the wheel are connected by universal joints.
The drive axle is at the end of the power transmission system, and its basic functions are: (1) transmitting the engine torque from the universal transmission device to the drive wheel through the main reducer, differential, half shaft, etc., to reduce speed and increase torque; (2) Change the transmission direction of torque through the bevel gear pair of the main reducer; (3) The differential realizes the differential of the wheels on both sides to ensure that the inner and outer wheels steer at different speeds; (4) The bearing and torque transmission functions are realized through the bridge shell and wheels.
The drive axle design should meet the following basic requirements:
1. The main reduction ratio selected should ensure that the car has the best power and fuel economy.
2. The overall dimension should be small, and the necessary ground clearance should be ensured. It mainly refers to the size of the main reducer as small as possible.
3. Gears and other transmission parts work smoothly and have low noise.
4. High transmission efficiency under various speeds and loads.
5. Under the condition of ensuring sufficient strength and stiffness, the mass should be small, especially the unsprung mass should be as small as possible to improve the smoothness of the car.
6. Coordinate with the movement of the suspension guide mechanism, and for the steering axle, it should also coordinate with the movement of the steering mechanism.
7. Simple structure, good processing technology, easy manufacturing, easy to disassemble and adjust.